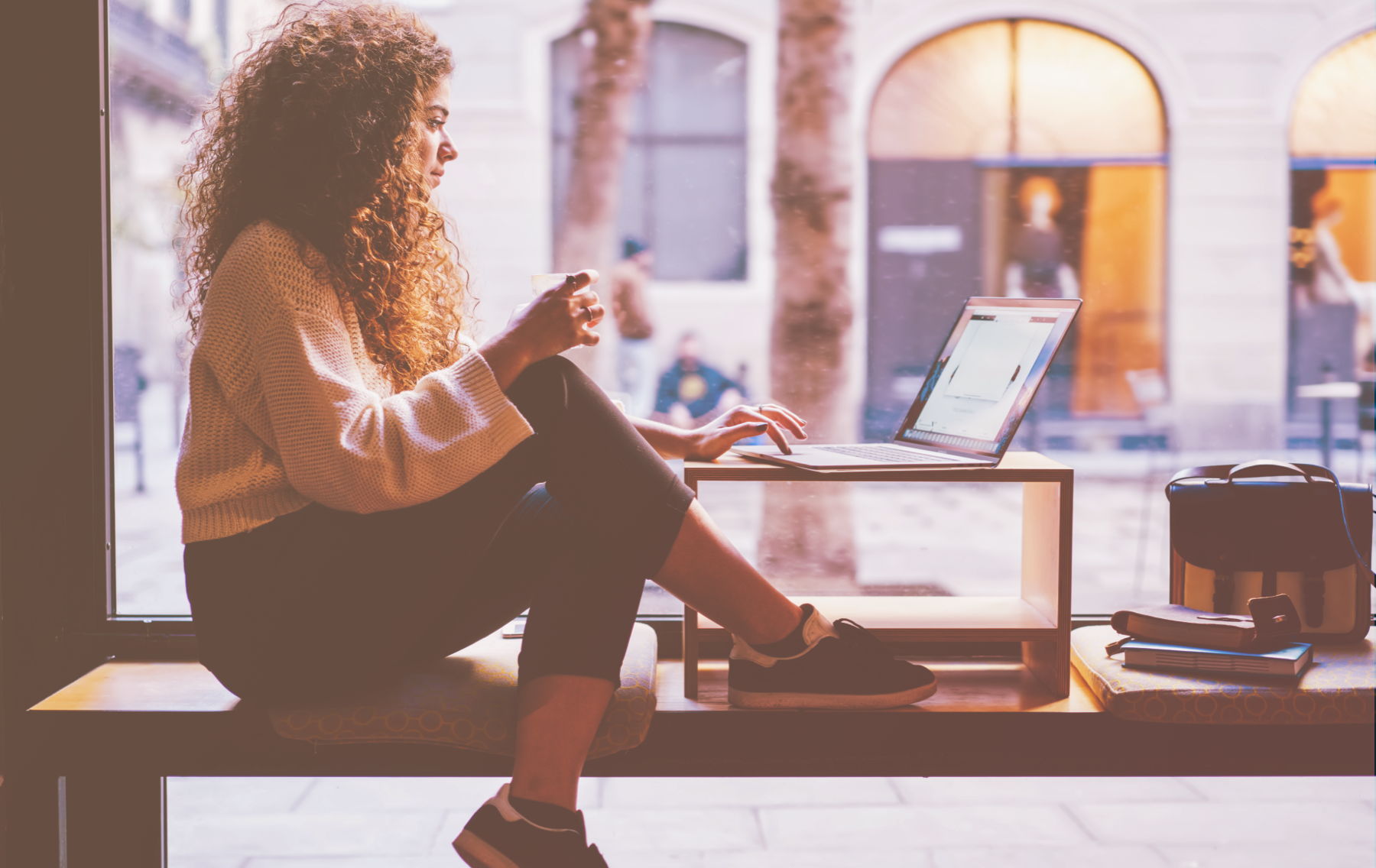
It is important to be acquainted with the different means of verifying bank accounts before starting an international money transfer. IBAN and routing numbers are two of the most popular options. Yet, what exactly are they and how do they function? Let’s delve into the matter in this article! Scroll down to read more.
IBAN or Routing Number: What Do They Mean?
While both the International Bank Account Number (IBAN) and the routing number (RN) serve to uniquely identify a bank account and ensure that funds are sent to the correct recipient, they do it in somewhat different ways.
IBAN is widely used in other areas of the world and was created to facilitate the handling of international financial transactions. Conversely, RTN is an identifying scheme that solely includes institutions within the United States.
If the receiving country uses it, an international bank account number (IBAN) and other information about the recipient’s bank account are required to complete a transfer from the United States to another country.
What is an IBAN?
The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is a universally accepted method of identifying financial accounts in different countries. It may have anywhere from 8 to 34 alphabetic and numeric digits and is widely used in places besides the United States. The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) was established to standardise and facilitate banking operations across borders.
IBANs follow a variety of different formats depending on the jurisdiction, but they always consist of a bank code, a country code, an account number, and a check digit. For some sorts of transactions, such as SEPA payments within the European Union, an IBAN is necessary. IBANs are used for both incoming and outgoing international transfers.
How Does an IBAN Work?
IBAN is used in conjunction with the account number and other account-identifying information to verify the transaction’s specifics, such as the destination country, bank, branch, and the recipient’s unique account number. An international bank account number (IBAN) is used to validate the recipient’s account and initiate a transfer from your bank to that account.
How Does an IBAN Look Like?
The maximum length of an IBAN in any given nation is 34 alphanumeric characters.
The first two characters indicate the nation, such as GB for Great Britain or PT for Portugal.
The following code may be validated thanks to the inclusion of check digits.
The final three to a maximum of thirty characters make up the beneficiary’s “Basic Bank Account Number,” which may contain the bank, branch, and account number. Several zeroes are appended to some IBANs to make up for the length of the country code.
What is a Routing Number?
A nine-digit identifier, a “routing number,” is used to identify a certain bank in the United States. Direct deposits, electronic payments, and wire transfers are only some of the common types of domestic use. Each bank that uses the ACH network has a unique routing number that has been allocated to it by a Federal Reserve Bank.
During a financial transaction, a routing number is used to ensure that money is sent to the proper financial institution. The first four digits of a bank’s routing number designate the local Federal Reserve district, whereas the last four designate the individual branch. The last digit of a routing number is a check digit that ensures the number is entered correctly.
How Does a Routing Number Work?
Every single bank in the United States has a unique routing number that is managed by the American Bankers Association and Accuity. Every financial institution is assigned at least one and no more than four unique routing numbers. Depending on the bank and the kind of transfer being made, the routing transit number (RTN) may be different for each of the states in which the bank operates.
Banks and individual accounts both have unique routing numbers, however, the latter does not always correspond with the account number. Several types of accounts at the same bank, such as checking and savings, may have the same routing number.
How Does a Routing Number Look Like?
A 9-digit code used to identify a specific American bank, often called a bank identification number, a routing number consists of three parts:
- The Federal Reserve Routing Symbol (the first four numbers) designates the specific branch of the financial institution.
- As with the third and fourth characters of an IBAN, the ABA institution identifier consists of the bank routing the transaction, the check processing centre, and the Federal Reserve district where the bank is headquartered.
- The final digit is the check digit, which ensures that there are no mistakes in the transaction.
What are the Key Differences between IBAN and Routing Numbers?
- While both the IBAN and the routing number serve to identify bank accounts, there are significant variations between the two:
- Both routing numbers and IBANs are utilised in the United States, although IBANs are predominantly used in countries outside the United States.
- The maximum length for an IBAN is 34 characters, whereas the minimum length for a routing number is 9.
- IBANs follow a format that varies by nation, but routing numbers in the United States follow a uniform format used by all financial institutions.
- For some sorts of foreign transactions, an IBAN is necessary, while routing numbers are mostly used for local transactions.
In conclusion, both International Bank Account Numbers (IBANs) and routing numbers (routing transit numbers) may be used to identify specific bank accounts. Instead of using a routing number, which is solely utilised in the United States, you should use an international bank account number (IBAN). While routing numbers are uniform across all financial institutions in the United States, IBANs are often lengthier and have a unique format that differs by nation. Each time money is being sent across borders, whether globally or domestically, it’s important to know the distinctions between the two techniques.